What is Integrative Manual Therapy? ‒ An In-Depth Exploration
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) skillfully blends manual techniques with somatic experiencing‚ addressing the interconnectedness of body and mind for holistic wellness.
This approach utilizes palpation‚ soft tissue work‚ and joint mobilization‚ often complementing other therapies within a broader‚ integrative care framework.
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) represents a sophisticated and evolving approach to healthcare‚ moving beyond traditional manual techniques to encompass the whole person – body‚ mind‚ and spirit. It’s a system built on the understanding that physical structures and emotional experiences are deeply intertwined‚ and that addressing one without the other often yields incomplete results.
IMT isn’t simply about “fixing” a problem; it’s about restoring the body’s natural ability to heal itself by releasing restrictions and imbalances. This is achieved through highly skilled palpation and a variety of soft tissue manipulation and joint mobilization techniques. However‚ what truly sets IMT apart is its integration of somatic experiencing‚ recognizing the impact of past trauma and emotional holding patterns on physical pain and dysfunction.
Essentially‚ IMT seeks to facilitate a deeper level of body awareness‚ allowing individuals to reconnect with their innate wisdom and capacity for self-regulation. It’s a powerful modality for those seeking lasting relief from chronic conditions and a more profound sense of well-being.
The Core Principles of IMT
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) operates on several fundamental principles. Firstly‚ the body possesses an inherent self-correcting mechanism; IMT aims to remove obstacles hindering this natural process. Secondly‚ structure and function are inextricably linked – addressing structural imbalances directly impacts physiological function‚ and vice versa.
A crucial tenet is the mind-body connection. IMT acknowledges that emotional trauma and chronic stress manifest physically‚ creating patterns of tension and restriction. Therefore‚ treatment isn’t solely focused on the musculoskeletal system but considers the individual’s emotional landscape.
Palpation is central‚ allowing the therapist to precisely identify areas of restriction and dysfunction. IMT emphasizes a gentle‚ respectful approach‚ working with the body’s responses rather than forcing change. Finally‚ integrative care is paramount – IMT is often most effective when combined with other therapies‚ fostering a holistic and personalized treatment plan.

Historical Development of Integrative Manual Therapy
IMT evolved from traditional manual therapy and osteopathy‚ expanding to incorporate somatic experiencing and a holistic view of trauma’s impact on the body.
Origins in Manual Therapy and Osteopathy
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) finds its roots deeply embedded within the established fields of manual therapy and osteopathy. These disciplines historically focused on the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal imbalances through hands-on techniques. Manual therapy‚ as a broader category‚ encompasses the manipulation of soft tissues and joints to alleviate pain and restore function.
Osteopathy‚ originating in the late 19th century‚ further emphasized the interconnectedness of the body’s systems and the body’s self-healing capabilities. Both approaches relied heavily on skilled palpation to identify areas of restriction and dysfunction. However‚ IMT distinguishes itself by moving beyond purely structural correction. It acknowledges the significant influence of psychological and emotional factors‚ building upon these foundational manual techniques to address the whole person.
Early pioneers in manual medicine laid the groundwork for IMT’s integrative philosophy‚ recognizing that physical symptoms often have complex origins.
The Evolution Towards an Integrative Approach
The progression towards Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) represents a significant shift in perspective from traditional manual methods. Recognizing the limitations of solely addressing biomechanical issues‚ practitioners began exploring the profound impact of trauma and emotional holding patterns on the body. This led to the incorporation of somatic experiencing – a therapeutic approach that focuses on resolving trauma through body awareness and self-regulation.
This evolution acknowledges that chronic pain and dysfunction are often rooted in unresolved emotional experiences. IMT integrates these principles‚ utilizing manual techniques not just to release physical tension‚ but also to facilitate the release of stored trauma within the tissues.
Furthermore‚ the rise of integrative care models emphasized the importance of considering the patient as a whole – mind‚ body‚ and spirit – fostering a more comprehensive and effective treatment approach.

Key Components of Integrative Manual Therapy
IMT centers around skilled palpation‚ precise soft tissue manipulation‚ and gentle joint mobilization‚ all interwoven with a deep understanding of the body’s interconnectedness.
Palpation and Assessment Techniques
Palpation forms the cornerstone of Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) assessment‚ extending far beyond simply identifying tender points. Therapists employ highly refined tactile skills to map the intricate landscape of soft tissues – muscles‚ fascia‚ ligaments – discerning subtle changes in texture‚ temperature‚ movement‚ and tone.
This detailed mapping isn’t merely structural; it seeks to understand how these tissues relate to the body’s overall biomechanics and‚ crucially‚ to the patient’s lived experience. Assessment goes beyond localized pain‚ investigating patterns of restriction and compensation throughout the entire system. Rhythmically assessing soft tissue structures is key.
IMT practitioners don’t just feel for problems; they listen with their hands‚ interpreting the body’s subtle communication. This comprehensive approach allows for a uniquely individualized treatment plan‚ addressing the root causes of dysfunction rather than simply treating symptoms. The goal is to understand the body’s story‚ revealed through touch.
Soft Tissue Manipulation
Soft tissue manipulation within Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) is a nuanced process‚ differing significantly from standard massage. Therapists utilize a variety of techniques – myofascial release‚ muscle energy techniques‚ and positional release – applied with precise pressure and direction‚ guided by the findings from detailed palpation.
The focus isn’t simply on relieving muscle tension‚ but on restoring optimal tissue length‚ reducing fascial restrictions‚ and improving fluid dynamics. These techniques aim to release chronic holding patterns and address the underlying causes of pain and dysfunction.
IMT recognizes the interconnectedness of the body; therefore‚ soft tissue work isn’t confined to the area of pain. Therapists may address restrictions in distant tissues that are contributing to the problem. This holistic approach‚ combined with a deep understanding of anatomy and biomechanics‚ allows for effective and lasting results.
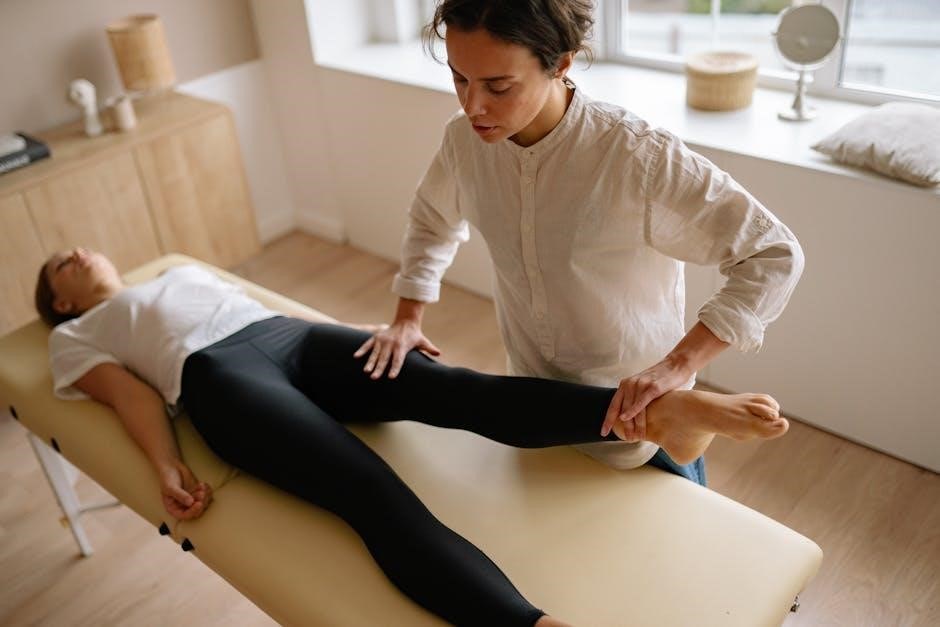

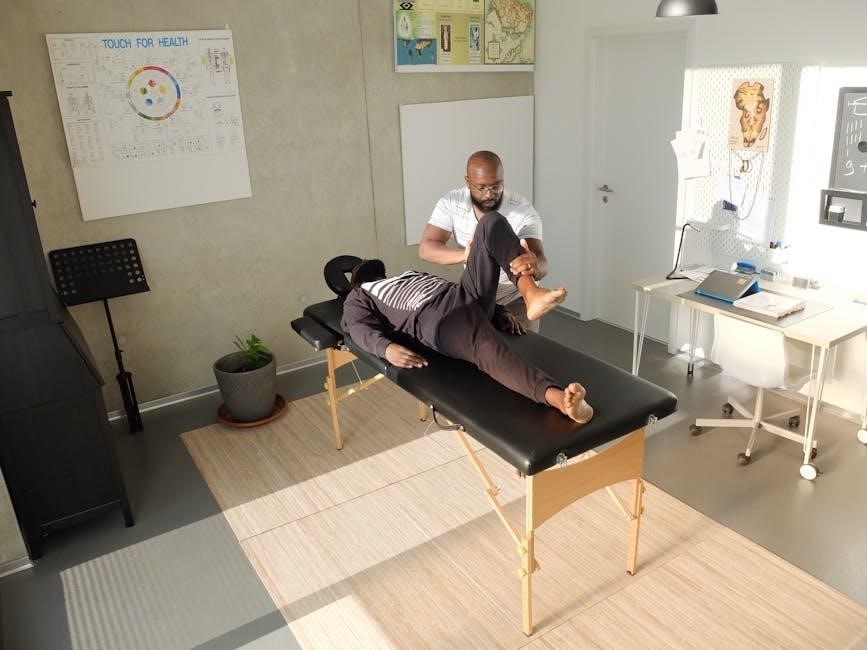
Joint Mobilization and Manipulation
Joint mobilization and manipulation‚ integral to Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT)‚ are applied with a refined understanding of joint biomechanics and neurophysiology. Unlike forceful adjustments‚ IMT prioritizes gentle‚ rhythmic movements designed to restore proper joint motion and reduce restrictions.
Therapists carefully assess joint play – the subtle movements available within a joint – to identify areas of dysfunction. Mobilization techniques involve graded oscillations to improve range of motion‚ while manipulation utilizes a quicker‚ smaller amplitude thrust.
However‚ these techniques are always integrated with soft tissue work and somatic awareness exercises. IMT recognizes that joint dysfunction often stems from surrounding tissue restrictions and altered movement patterns. The goal isn’t simply to ‘fix’ the joint‚ but to restore optimal movement and function throughout the entire kinetic chain.

IMT vs. Traditional Manual Therapy
IMT distinguishes itself through a holistic‚ body-centered approach‚ integrating somatic experiencing alongside traditional techniques‚ unlike conventional manual therapy’s primarily structural focus.
Distinguishing Features of Integration
Integrative Manual Therapy’s core difference lies in its comprehensive view of the patient‚ moving beyond merely addressing musculoskeletal issues. It acknowledges the profound impact of trauma and emotional states on physical pain and dysfunction. Unlike traditional manual therapy‚ which often focuses on biomechanical correction‚ IMT incorporates somatic experiencing – a technique that helps release stored trauma within the body.
This integration allows therapists to address not just where the pain is‚ but why it exists‚ considering the interplay between the nervous system‚ emotional patterns‚ and physical structures. Facilitatory and inhibitory techniques are thoughtfully applied‚ mapping soft tissue structures rhythmically. The approach emphasizes enhancing body awareness‚ fostering a mind-body connection‚ and utilizing manual treatment to amplify the benefits of other therapies‚ creating a truly holistic treatment plan.
The Role of Somatic Experiencing in IMT
Somatic Experiencing (SE) is a pivotal component of Integrative Manual Therapy‚ addressing the physiological impact of trauma that often underlies chronic pain and dysfunction. SE recognizes that trauma can become “stuck” within the body‚ manifesting as physical tension‚ restricted movement‚ and heightened sensitivity. It’s a body-centered therapy combining talk therapy with gentle physical techniques.
Within IMT‚ SE isn’t about reliving the traumatic event‚ but rather about gently releasing the trapped energy and restoring the body’s natural self-regulation abilities. Therapists guide patients to notice subtle sensations‚ fostering a sense of safety and allowing the nervous system to complete defensive responses that were interrupted during the original trauma. This process enhances body awareness and facilitates a deeper integration of mind‚ body‚ and spirit‚ leading to lasting healing.
Conditions Commonly Treated with IMT
IMT effectively addresses chronic musculoskeletal pain‚ TMJ disorders‚ and trauma-related pain‚ offering relief and improved function through holistic‚ body-centered interventions.
Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
Chronic musculoskeletal pain‚ a pervasive issue‚ often benefits significantly from Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT). Unlike solely focusing on symptom management‚ IMT investigates the root causes of pain‚ considering the interplay between tissues‚ nerves‚ and the body’s overall mechanics.
Through precise palpation and soft tissue manipulation‚ therapists identify restrictions and imbalances contributing to discomfort. Joint mobilization restores proper movement patterns‚ reducing strain and alleviating pain. Importantly‚ IMT acknowledges the mind-body connection; past trauma or emotional stress can manifest as physical pain.
By integrating somatic experiencing‚ IMT helps release stored tension and promote a sense of safety within the body. This holistic approach‚ often combined with educational programs like back pain schools‚ empowers patients to manage their pain effectively and regain functional capacity‚ offering a path towards lasting relief and improved quality of life.
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) disorders frequently respond well to Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT)‚ which addresses the complex relationship between jaw mechanics‚ facial structures‚ and the nervous system. IMT goes beyond simply treating jaw pain; it explores contributing factors like posture‚ breathing patterns‚ and emotional tension.
Therapists utilize skilled palpation to identify restrictions in the jaw muscles‚ ligaments‚ and surrounding tissues. Gentle soft tissue manipulation releases tension‚ while precise joint mobilization restores optimal movement within the TMJ. Recognizing the impact of systemic factors‚ IMT considers the broader context of the patient’s health.
Integrative care approaches‚ combining IMT with other therapies‚ can address underlying imbalances. Furthermore‚ IMT acknowledges the potential link between trauma and TMJ dysfunction‚ utilizing techniques to promote nervous system regulation and facilitate healing‚ offering a comprehensive path to relief.
Post-Traumatic Stress and Trauma-Related Pain
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) offers a sensitive and effective approach to addressing post-traumatic stress (PTSD) and the chronic pain often associated with trauma. Recognizing that trauma is stored within the body‚ IMT utilizes gentle techniques to release physical tension and restore nervous system regulation.
IMT therapists understand that trauma can manifest as restrictions in the fascia‚ muscles‚ and joints. Through careful palpation and soft tissue manipulation‚ they work to unlock these patterns of holding‚ promoting a sense of safety and grounding. The integration of somatic experiencing principles is crucial‚ allowing the body to process and release trapped trauma.
This integrative care model acknowledges the mind-body connection‚ offering a pathway to healing that addresses both the physical and emotional impacts of trauma‚ fostering resilience and well-being;
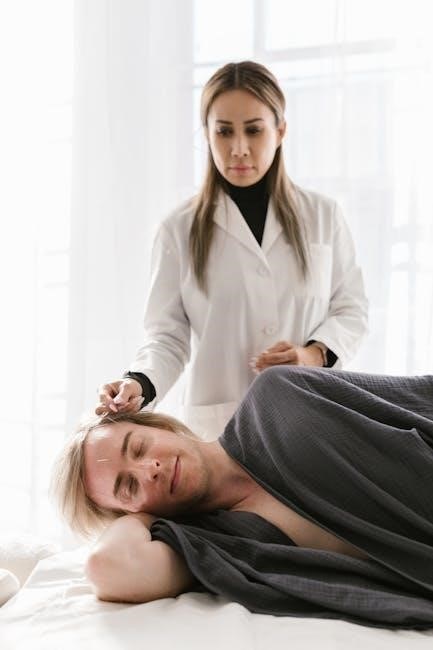

The Benefits of Integrative Manual Therapy
IMT delivers significant pain relief‚ improves physical function‚ and cultivates heightened body awareness‚ fostering a profound mind-body connection for lasting wellness.
Pain Relief and Improved Function
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) excels at alleviating chronic musculoskeletal pain‚ offering a pathway to restored movement and diminished discomfort. By addressing the root causes of pain – often stemming from interconnected bodily systems – IMT goes beyond merely masking symptoms.

The skilled application of manual therapy techniques‚ including soft tissue manipulation and joint mobilization‚ releases restrictions and restores optimal biomechanics. This‚ in turn‚ enhances function‚ allowing individuals to regain ease and efficiency in their daily activities.
Furthermore‚ IMT’s integration of somatic experiencing acknowledges the role of trauma and emotional holding patterns in chronic pain. Releasing these deeply held tensions contributes to both immediate pain relief and long-term improvements in physical capabilities‚ promoting a more comfortable and active lifestyle. It’s effective in treating LBP.
Enhanced Body Awareness
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) cultivates a profound connection between mind and body‚ fostering enhanced body awareness. Through gentle‚ focused touch and skilled palpation‚ practitioners guide patients to perceive subtle sensations and recognize patterns of tension often overlooked.
This heightened awareness isn’t simply about noticing discomfort; it’s about understanding how the body holds and expresses experiences – both physical and emotional. IMT encourages individuals to become active participants in their healing process‚ learning to identify and address imbalances before they escalate into pain or dysfunction.
By restoring the body’s natural ability to self-regulate‚ IMT empowers patients to move with greater ease‚ efficiency‚ and mindful presence. This improved proprioception – the sense of body position – contributes to better posture‚ coordination‚ and overall well-being‚ promoting a deeper sense of embodiment;
Integration of Mind-Body Connection
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) fundamentally recognizes the inseparable link between mental and physical states‚ prioritizing the integration of mind-body connection. Unlike purely mechanical approaches‚ IMT acknowledges that trauma‚ stress‚ and emotional patterns can manifest as physical restrictions and pain.
Drawing upon principles of somatic experiencing‚ practitioners facilitate a safe exploration of these embodied memories‚ allowing the nervous system to release stored tension and complete interrupted responses. This process isn’t about reliving trauma‚ but rather about gently restoring balance and resilience.
By addressing the root causes of dysfunction – often residing in the interplay between mind and body – IMT promotes lasting healing and prevents recurrence. This holistic perspective fosters a deeper understanding of oneself‚ empowering individuals to navigate life’s challenges with greater ease and emotional regulation.
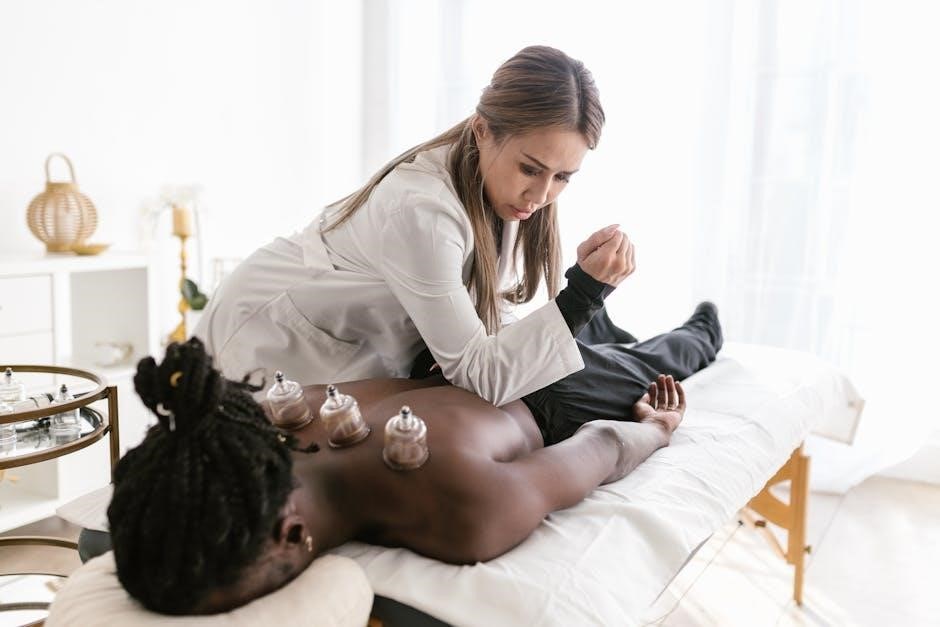

IMT as Part of Integrative Care
IMT thrives within integrative care‚ seamlessly combining with therapies like talk therapy and educational programs for comprehensive‚ patient-centered healing and lasting relief.
Combining IMT with Other Therapies
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) doesn’t operate in isolation; its strength lies in synergistic collaboration with diverse therapeutic modalities. Effectively addressing chronic musculoskeletal pain‚ for example‚ often benefits from pairing IMT with a back pain school‚ empowering patients with self-management strategies.
Furthermore‚ the profound mind-body connection emphasized in IMT makes it a valuable adjunct to somatic therapy‚ where talk therapy is interwoven with physical techniques. This combination can be particularly impactful in resolving trauma-related pain and addressing the complex needs of individuals experiencing post-traumatic stress.
The ability of manual treatment to enhance other interventions – functioning effectively before‚ during‚ or after – underscores its versatility. A holistic treatment plan‚ thoughtfully integrating IMT alongside conventional medical approaches‚ yields optimal outcomes‚ fostering comprehensive well-being and sustained improvements in function.
The Importance of a Holistic Treatment Plan
Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) thrives within a holistic framework‚ recognizing that true healing extends beyond symptom management. A comprehensive treatment plan acknowledges the intricate interplay between physical‚ emotional‚ and even spiritual dimensions of health‚ particularly when addressing conditions like Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) disorders.
Considering the etiopathogenesis – the origin and development of disease – from multiple perspectives‚ as seen in integrative areas of medicine‚ is crucial. Simply manipulating soft tissues isn’t enough; addressing underlying trauma‚ stress‚ or emotional patterns is often essential for lasting relief.
This approach necessitates collaboration‚ potentially combining IMT with talk therapy‚ exercise rehabilitation‚ and lifestyle modifications. Such a plan isn’t merely additive; it’s synergistic‚ where each component enhances the effectiveness of the others‚ fostering a more profound and sustainable path to wellness.

Finding a Qualified Integrative Manual Therapist
Seeking a therapist with proper certification and training is vital; ensure they possess a deep understanding of somatic experiencing and manual techniques.
Expect a thorough assessment and personalized sessions focused on restoring balance and addressing your unique needs.
Certification and Training
Locating a truly qualified Integrative Manual Therapist necessitates careful investigation into their educational background and credentials. While the field is evolving‚ specific standardized certifications are emerging as benchmarks of competency. Thorough training programs emphasize a deep understanding of anatomy‚ physiology‚ and biomechanics‚ forming the foundation for effective assessment and treatment.
Crucially‚ comprehensive IMT training extends beyond traditional manual therapy techniques. It incorporates somatic experiencing principles‚ equipping therapists to address the interplay between physical sensations‚ emotional patterns‚ and the nervous system. Look for practitioners who have completed extensive coursework and supervised clinical hours‚ demonstrating proficiency in palpation skills‚ soft tissue mobilization‚ and joint mobilization techniques. Continuing education is also paramount‚ ensuring therapists remain current with advancements in the field and refine their clinical expertise.
What to Expect During a Session
An initial session typically begins with a detailed health history and a thorough postural and movement assessment. The therapist will utilize skilled palpation to identify areas of restriction‚ tension‚ and asymmetry within the body’s fascial system. Expect gentle‚ yet focused‚ manual techniques applied to soft tissues and joints‚ aiming to restore optimal biomechanical function.
Unlike some traditional approaches‚ IMT prioritizes a collaborative approach‚ with the therapist continually checking in with your subjective experience. You may be asked to notice subtle shifts in sensation‚ breath‚ or emotional state during the treatment. Sessions are often described as deeply relaxing and restorative‚ promoting increased body awareness and a sense of integration. The length of a session can vary‚ but generally ranges from 60 to 90 minutes‚ tailored to individual needs.